There could be more to these design patterns and its applicability in SilverLight, however this article is only intended to present and overview and high-level understanding of how to get started in SilverLight application patterns.
SilverLight implements SOLID design guidelines along with a MVVM or MVP design pattern.
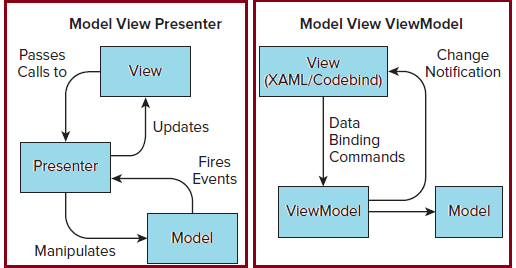
Figure shown below depicts the comparison of approaches followed in MVVM and MVP pattern.
MVVM pattern can follow two approaches
1. View First: The view is responsible for creating an instance of a ViewModel, via databinding to a static resource or setting the data context in the code-behind file.
- Databinding approach
UserControl.Resources
local:SampleViewModel x:Key=”ViewModel” /
UserControl.Resources
Grid DataContext=”{Binding Path=Object,
Grid is bound to object that is obviously in Model.
- Code Behind approach
2. View-Model first: The ViewModel creates an instance of the view and sets its data context.
This is usually done using an Inversion of Control Container like MEF, PRISM etc.
(This article is only an exploration of design patterns in use in silverlight)
Both these approaches have their own pros and cons that I am not going to discuss here. For the time it’s your decision based on requirement as to which approach you want to follow.
Event Broker Pattern:
The normal way to use an event is for one class to subscribe to the events of another class. This approach works great when each class has direct access to the other and only one class can trigger an event.
However, in more advanced scenarios one or more classes may need to send the same event or be notified by events without subscribing directly to the caller event.
Events can be treated as another type of dependency and instead of subscribing directly to an event, a container (Event Broker) could be used to manage the subscribers and publishers of an event. This is exactly what is done in IOC /Dependency injection .
When an event occurs, the Event Broker would be responsible for notifying all subscribers that an event occurred.
Let’s consider a practical example of handling the closing of an application.
Normal Scenario: The application needs to loop through each control on the screen to check to see if its needs to be saved before applications closes.
Event Broker Pattern Scenario:
Event Broker handles notification to each control, to save itself. Isn’t his a better approach.
Hope this was helpful.
Till Next we connect……
Happy reading……
Comments
Post a Comment